Insights, Products
RCS vs iMessage: What’s the difference?

Whether you’re Team iPhone or Team Android, it doesn’t really matter anymore. At least when it comes to messaging.
For a long time, messages sent between iPhones and Androids defaulted to traditional SMS. SMS is reliable and reaches every mobile phone on the planet (that’s over seven billion people!). With its instant delivery straight to a phone’s native messaging inbox, no extra apps, and no sign-ups needed, SMS is easy and to-the-point. But now, SMS has to share its spotlight.
With Apple’s new support for Rich Communication Services (RCS) on iOS, more messages can be rich and interactive. Just like before, the messages land in a user’s native mobile inbox – only now, fewer are basic text messaging, and more are dynamic RCS content.
In this article, we’ll compare RCS vs iMessage for personal communication now that Apple supports RCS. We’ll also look at Apple and Google’s business messaging solutions and help you decide which is best for your strategy.
RCS vs iMessage for P2P messaging: Understanding the basics
Let’s first look at Google and Apple’s person-to-person (P2P) messaging solutions: RCS and iMessage.
Both RCS and iMessage have over a billion users each and function similarly to popular over-the-top (OTT) messaging platforms like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger. But the key difference? They don’t require users to download an additional app or create a new account. Instead, they work within the framework of a user’s native messaging inbox. They support rich media, like high-quality images and videos, and offer features like read receipts and typing indicators. While both RCS messages and iMessages travel over Wi-Fi or a mobile data connection, they can fall back to SMS if this connection isn’t available.
What is Rich Communication Services (RCS)?
RCS is a modern messaging protocol developed by the GSM Association (GSMA) to upgrade SMS and MMS. It delivers a rich messaging experience that includes videos, images, voice memos, maps, and more.
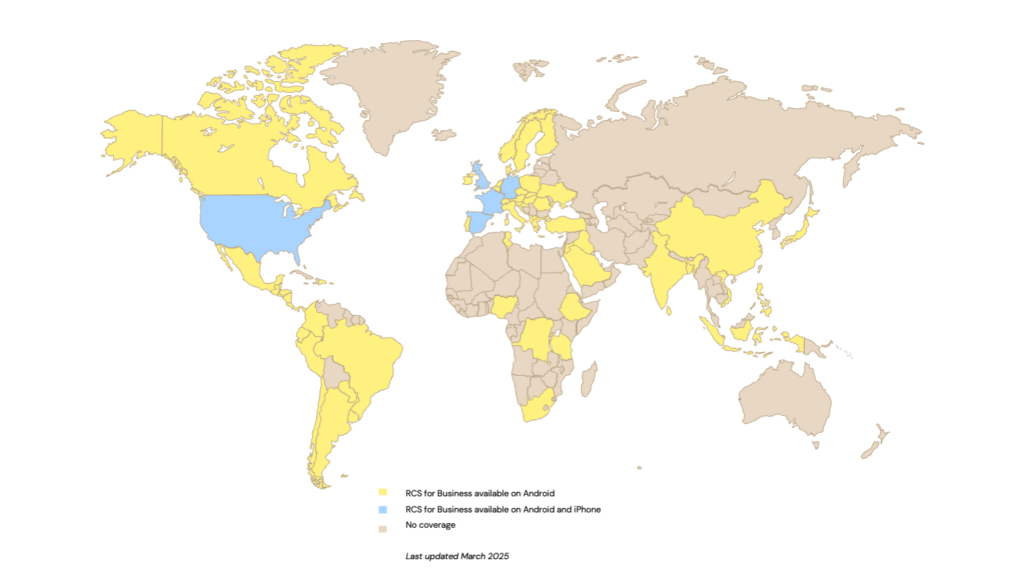
Until 2024, RCS messaging was limited to Android phones. With iOS 18, Apple introduced RCS support for P2P messaging in select markets, expanding further with iOS 18.5. There are a number of different carriers that support RCS messaging on iPhones in select markets.
This means richer messaging experiences for Android and Apple users who are messaging each other, including features like read receipts, typing indicators, and better group chat experiences, regardless of their mobile operating system.
There are 3.9 billion Android users worldwide, with devices from manufacturers like Samsung, Google, and OnePlus. While not all of these devices have RCS enabled, it’s worth noting that RCS is the default messaging app on most new devices that run Android OS. Google reports that over one billion monthly active users have RCS enabled, and it has strong support from global mobile operators.
What is iMessage?
iMessage is Apple’s proprietary instant messaging service for iOS devices like iPhones, iPads, and Macs. It supports text, photos, multimedia, voice memos, locations, videos, and more, which are all transmitted over an internet connection or cellular data. iMessages are always end-to-end encrypted and appear in blue text bubbles on Apple devices.
Apple says over two billion users actively use its hardware. Apple devices are particularly popular in countries like Japan, the United States, and Australia for all ages up to 65.
iMessage is exclusive for Apple devices, so if an iPhone user messages someone with an Android, RCS is possible if it’s enabled; otherwise, the message defaults to SMS.
Comparing RCS vs iMessage
When it comes to functionality for P2P messaging, both RCS and iMessage include rich messaging experiences. However, there are a few notable differences between the two.
Here’s a quick comparison chart of RCS vs iMessage for P2P messaging:
| Feature | RCS | iMessage |
| Operating system compatibility | Android and iOS 18 (subject to market and carrier support) | iOS (iPhones, iPads, Macs) |
| Message transmission | Cellular data or Wi-Fi | Cellular data or Wi-Fi |
| Message security | Encrypted in transit; end-to-end between Android devices (i.e. via Google Messages) | End-to-end encrypted in Apple’s ecosystem |
| Fallback to SMS | Yes, when RCS is unavailable | Yes, when Apple’s iMessage isn’t available |
| Message features | Rich media, typing indicators, read receipts | Rich media, typing indicators, reactions, read receipts |
| Message bubble color | No standard (varies by app and platform) | Blue text bubbles |
While both channels enhance the user experience beyond text messages, RCS doesn’t yet have end-to-end encryption across messaging services, though Apple has confirmed that the Universal Profile 3.0, which supports end-to-end encrypted RCS messaging, will be available in a future iOS update. On the other hand, iMessage offers end-to-end encryption for P2P messages but is limited to Apple devices.
“In the not-so-distant future, end-to-end encryption will be supported on both iOS and Android devices, ensuring messages will remain private and protected regardless of the messaging technology a user is communicating from.”

Is RCS messaging better than iMessage?
With Apple’s adoption of RCS on iOS, you might wonder if RCS somehow has an advantage over iMessage. But it’s not that simple.
Both RCS and iMessage have their strengths and appeal to different user groups. For example, iMessage dominates in markets like the U.S., where Apple holds around 60% market share. But globally, Android leads with over a 70% global market share, so if you’re trying to reach someone using a non-Apple device, you’ll likely use RCS.
RCS and iMessage are both popular for P2P messaging, but Google and Apple also have business messaging solutions to help you reach your audience in the best possible ways.
Now that Apple supports RCS on iPhones, will RCS replace iMessage someday? Not quite. In this short video, Miriam Liszewski, RCS Product Manager at Sinch, explains how RCS will continue to complement, rather than replace, iMessage.
RCS for Business vs Apple Messages for Businesses
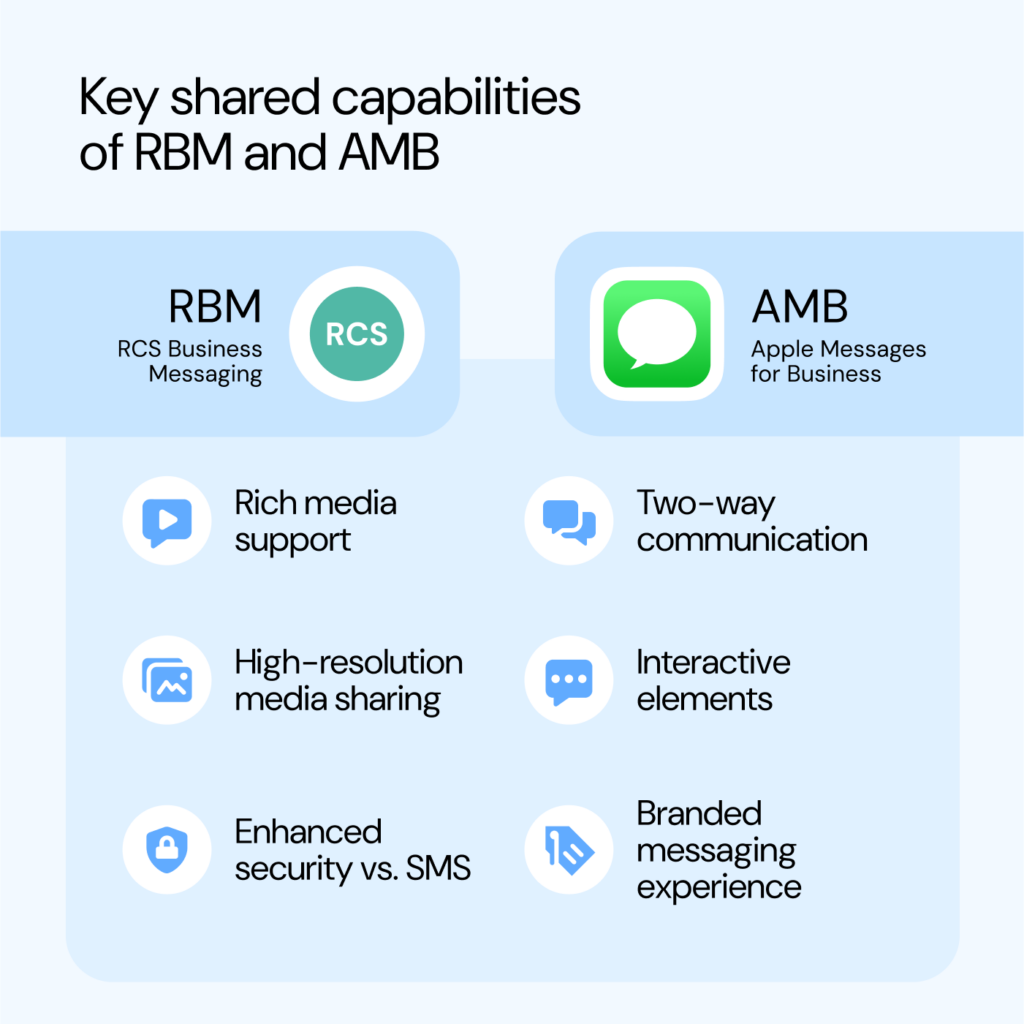
Customers expect messaging with brands to feel as easy and trusted as texting a friend. According to our 2025 State of customer communications report, 30% of consumers want promotional messages via text messaging, while 42% are more likely to trust messages that include visual indicators like logos or verified badges. RCS for Business and Apple Messages for Business (AMB) both deliver interactive features that meet these expectations, giving brands a more secure, engaging way to connect.
What is RCS for Business?
Google’s RCS for Business solution (previously called RBM) lets businesses communicate with subscribers with interactive messages that feel similar to chat apps. But unlike popular apps, RCS works within the native messaging app on a user’s smartphone.
RCS for Business offers a few different message types for businesses to reach customers with branded messaging. These vary in cost and have different supported features but all offer improvements over SMS messages.
In 2025, our research found that 87% of business leaders across healthcare, financial services, retail, and tech are at least somewhat familiar with RCS – and 59% believe it will be game-changing for business messaging.
What is Apple Messages for Businesses (AMB)?
Apple Messages for Business (AMB) lets users message businesses from their phone, Mac, or Apple Watch. Only customers can initiate a conversation in AMB – businesses can’t send unsolicited messages. Once the conversation is deleted, businesses can’t re-engage unless the customer chooses to restart it.

AMB is designed for moments when customers are ready to connect, whether they’re booking an appointment or seeking support, and integrates with Apple Pay for in-conversation purchases. When a customer does reach out via AMB, businesses can respond with rich, engaging content like slideshows, videos, and more.
Violations of the Business Update guidelines (e.g., spammy content) can lead to permanent removal from the AMB channel.
Comparing RCS for Business and Apple Messages for Businesses
Google and Apple’s business messaging solutions cater to different customer needs. This chart shows how RCS vs AMB compare.
| RCS for Business | Apple Messages for Business (AMB) | |
| Platform compatibility | Android; iOS (subject to market and carrier support) | iOS |
| Business use case | Marketing, customer service, notifications | Customer support and inquiries – marketing is only possible if the end user messages the business first |
| How businesses start messaging end users | Similar to SMS; business must collect permission or opt-in before they can start messaging a user | Messages must be started by the end user. Businesses can only respond, and they need to have a live agent available during business hours |
| Encryption | Messages are encrypted between a user’s device and Google’s servers, and between Google’s servers and a messaging partner | Messages are encrypted between a user’s device and Apple’s servers, and when Apple transmits them to a business |
| Message experience | Includes rich media (images, GIFs, audio, videos) and branded messages that come from verified sender profiles | Includes interactive features and all the reactions, GIFs, file sharing, and more that are available in iMessage |
| Verified sender profiles | Yes; needed to implement a new sender agent | Yes; subject to Apple approval |
| Payment options | Yes, via Google Wallet | Yes, via Apple Pay |
| Cost | Varies between countries, suppliers, and use cases | Free, but brands need to connect to a Messaging Service Provider (MSP) to use |
When should brands use RCS for Business vs AMB?
Choosing between RCS for Business and AMB really comes down to your goals and your customers’ preferences. If you want to proactively reach out to customers with rich messaging, RCS is a great pick. But if your audience mostly uses Apple devices and prefers to initiate the conversation, AMB is the way to go.
Our advice? Focus on your customer base, the channels they use, and how each channel fits into your omnichannel marketing strategy. The right messaging platform can boost how you and your audience connect.
RCS for Business use cases
RCS conversational messages offer flexibility in how conversations are started. When a user responds to a brand’s RCS message within 24 hours, it’s considered an A2P (Application-to-Person) conversation. If the customer reaches out after 24 hours, it becomes a P2A (Person-to-Application) conversation.
RCS’s rich business features – like verified sender profiles and interactive elements – make it ideal for various use cases:
- Marketing campaigns (like Black Friday marketing)
- Location-based offers
- Abandoned cart reminders
- Customer newsletters
- Appointment reminders
- Critical notifications and one-time passwords
AMB use cases
AMB is designed for customer-initiated conversations. Users start conversations with businesses through entry points like Safari, Apple Maps, or directly from your own website. AMB is particularly strong for commerce because it integrates with Apple Pay so users can make in-conversation purchases. It’s ideal for enterprises that want to engage users right when they reach out.
Here are a few great use cases for AMB:
- Booking appointments
- Requesting product information
- Asking FAQs
- Reporting issues
- Customer support inquiries
It’s worth noting that launching on AMB requires end-to-end certification by Apple. This includes a comprehensive review of your brand’s entire implementation, from conversation flows and chatbot behavior to live agent handover processes.
And potential use cases may vary by region. For example, in North America, AMB recently introduced a new message type in their Business Messages API that lets businesses send proactive push notifications to subscribers through the Messages app.
Maximize your messaging strategy with RCS and AMB
Whatever your messaging goals, conversational messaging can greatly enhance your strategy by meeting customers where they are, in the apps that they already use and trust. While Apple Messages for Business offers a premium customer support experience, it also comes with strict technical, operational, and compliance requirements that may not be the right fit for most businesses.
That’s why we recommend exploring other rich messaging options like RCS or WhatsApp, which can deliver engaging, branded, and interactive experiences at scale. With the right approach, you can build a conversational experience that’s tailored to your audience, without the complexity.
For more guidance on conversational messaging, feel free to check out these additional resources:
- Could your marketing communications mix be working harder?
- 6 RCS campaign ideas to brighten your holiday marketing
- RCS for retail and ecommerce: Richer messages, better results
- Five easy ways to send WhatsApp promotional messages
- RCS marketing 101: Your complete guide for trusted, interactive messaging
- 10+ examples of mobile marketing campaigns to inspire you
When you’re ready to implement RCS or other messaging channels, integration is simple with Sinch Conversation API or Sinch Engage. Reach out to us to get started with optimizing your messaging strategy.