Insights
What is generative AI? Definition, use cases, and potential for businesses

From ChatGPT to DALL-E to Midjourney: Generative artificial intelligence (AI) suddenly seems to be everywhere. The technology has been called “transformative,” “revolutionary,” and “groundbreaking,” and everyone seems to agree that generative AI is the technology of the hour.
The Boston Consulting Group estimates that by 2025 generative AI will have a 30% share of the total AI market and be worth $60 billion.
If you’ve ever played around with tools like ChatGPT or Midjourney, it’s pretty easy to believe it. After all, generative AI is not only helpful, but also fun to use.
But aside from the hype around the new technology, what are the possibilities of generative AI for businesses? In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at the technology and explore how companies can use it effectively and safely.
What is generative AI?
Simply put, generative AI (GenAI) is a type of artificial intelligence that uses existing information to generate new content.
GenAI can generate text, images, and other types of media by using generative models. A generative model is an AI model that can distill patterns and structure from training data, and based on this information, generate new data that is very similar.
For example, you could feed a generative AI model images of dogs and cats, and – once the AI understands the data – it’ll be able to make thousands of new images of cats and dogs.
This has been a huge breakthrough for AI in terms of productivity and creativity.
The GPT revolution
While most of us heard about generative AI for the first time only a few years ago, it has been around for decades.
The first language model that used a neural network came about in 2001. It then took 16 years until Google created the first transformer model. OpenAI took this architecture and started developing different transformer models, until the infamous launch of ChatGPT in November 2022. The “T” in ChatGPT actually stands for transformer, so, ChatGPT still uses the underlying transformer technology today.
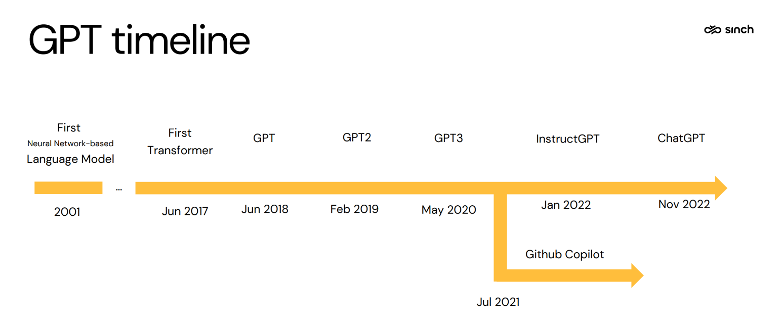
But if the technology has existed for so long, why did it take ChatGPT so long for its final breakthrough? Because ChatGPT was the first GenAI model that brought AI to the masses!
That’s why some have called it the “iPhone moment of AI.” Previous generative AI models weren’t giving users such a direct and personal command over the technology.
For instance, Netflix’ or Amazon’s recommendations for new shows to watch or interesting products to buy are also based on AI. However, as a user, you have limited control over the suggestions you get.
With ChatGPT, on the other hand, you can give very specific instructions and even tweak the results until you’re satisfied. That’s a whole new level of personalization and control.
“We’ve seen a shift from AI in product to AI for everyone. ChatGPT has put AI into the users’ hands.”
– Fréderic Godin, Head of AI, Sinch
How does generative AI work?
The foundation of generative AI is a prompt, which could be a text, an image, a video, musical notes, a design, or any other input that the AI system can process. AI algorithms then process the prompt and produce new output as a response.
In the early days of generative AI these prompts had to be fed via an API or through programming languages like Python.
That’s another reason why early versions of generative AI didn’t catch on with the wider public. Now, users can simply use plain language to create a prompt and even give feedback to optimize the answer.
What are DALL-E, ChatGPT, and Bard?
They’re all generative AI interfaces.
DALL-E was launched as a multimodal AI application by OpenAI for using prompts to generate images. The first version came out in 2021, then OpenAI launched a second version in 2022, and has since integrated the AI natively into its ChatGPT models.
ChatGPT was the “aha!” moment for generative AI. The chatbot from OpenAI can generate text based on plain language input by users. In 2019, Microsoft first invested in OpenAI and has now integrated a version of GPT into its Bing search engine.
Bard was Google’s transformer AI model. Its initial release was in March 2023. In the beginning Google didn’t release a public interface of Bard. However, when Microsoft added GPT to Bing, Google gave into the pressure and released a public version. In February 2024, Google unified Bard and Duet AI (another AI model Google used for its Workspace) under the Gemini brand.
In May 2024, Google announced that it would bring Gemini to its search.
Both Google’s and Microsoft’s public interfaces have faced criticism over inaccurate results and erratic behavior, and the companies have released updated versions since.
Recently, other tech companies like Meta have also come out with new generative AI interfaces like Meta AI.
What’s the difference between generative AI and conversational AI?
These two terms are often used interchangeably. Even though there are similarities, they refer to different branches of AI with different functions and abilities. Conversational AI focuses on making the interaction between bots and humans more natural.
The idea is to enable the bot through technologies like machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) and design practices like conversation design to “talk” like a human. Think of customer service chatbots or virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa known for their conversational abilities that assist people through a two-way conversation.

Generative AI on the other hand, enables users to create new content. It uses large language models (LLMs), machine learning algorithms and training data.
Aside from the different functions they serve, conversational AI and generative AI also operate differently. For instance, they both use training data, but they use it in different ways.
Conversational AI is trained on data sets with human language, so they can process the flow of a conversation and sound more natural when interacting with humans. Generative AI uses neural networks to identify patterns in its training data. They also process human feedback to generate more accurate responses.
While generative AI and conversational AI are different, they’re not mutually exclusive. In fact, many AI programs involve both. ChatGPT, for example, is a conversational chatbot in its smooth exchange with users, but it also generates content based on prompts.
What types of generative AI exist?
There are several focus areas for generative AI.
Text generation
Text programs like ChatGPT are the most common type of GenAI. They can come up with texts about pretty much any topic, write code, create questions, invent new recipes, or even summarize existing content.
Image generation
Generative AI programs like Midjourney specialize in creating images. They can either take an existing image and add new content to it, like swapping a person in an existing picture for a Santa Claus with a surfboard. What used to take a long time and require special design skills and expensive software can now be done in minutes by generative AI.
Image generation can also work from scratch, where a user gives specific instructions and the AI will create a new image based on the description.
Video generation
Similarly, generative AI can also take basic instructions and turn them into a video. Tools like Synthesia, OpenAI’s Sora, and Make-A-Video by Meta specialize in video generation.
This can be as simple as “make a video about a flying rocket” or as complex as setting up an onboarding video for new customers.
Music generation
Music generation is a relatively new field for GenAI. Programs like YouTube’s Dream Track, for example, can take instructions (“write a rap song in the style of T-Pain) or even create new songs or take existing music and re-write it for a specific instrument.
3D model generation
GenAI tools like Meshy specialize in creating 3D models. Users simply have to feed them text instructions or images and the AI can generate a 3D model. This can be helpful for designers or architects.
Drug discovery
People are now also starting to use generative AI outside content creation as the technology continues to improve. For example, healthcare researchers use generative AI to help them create medication based on the characteristics of existing diseases.
Given that generative AI is so versatile, there are also several use cases for businesses.
How can companies use generative AI?
Companies can use generative AI to support processes such as:
- Gathering and organizing large data sets
- Supporting marketing activities (inspiration for ad copy, personalized marketing campaigns, etc.)
- Training chatbots
- Optimizing and generating code
- Automating manual tasks (summarize long studies, write emails)
- Helping customer support
Overall, from automating manual tasks to reducing the amount of time spent writing to speeding up processes, generative AI has several benefits.
For a deep dive into the topic, check out our webinar about the potential of ChatGPT and other GenAI systems for businesses.
What are the limitations and risks of generative AI?
Even though generative AI has a lot of potential, businesses have to ensure secure usage. This ranges from data safety to legal security, but also includes strong codes of ethics for AI.
Lack of transparency
Many generative AI models aren’t very transparent. It’s very hard to determine where the generated information is coming from and if it’s even correct. And the AI also won’t tell the user when it just “invented” a plausible answer.
None of these scenarios are what you would want an AI to do for your business. After all, you don’t want the AI to make up a price or sell customers a product you don’t even offer. That’s neither good for your customers nor for your business.
Wrong expectations
It’s also important to point out that there might be false expectations when it comes to generative AI. Many might think that the AI “understands” things. It doesn’t. If you ask it if two pounds of feathers are heavier than two pounds of iron, it’ll probably find the correct answer, but this doesn’t mean that it understood the principle of weight.
If your customers aren’t aware of these limitations, they’ll have expectations that the AI can’t meet, which could lead to a bad user experience that’ll reflect negatively on your brand.
Prejudices
Also keep in mind that without any safeguards in place, generative AI will repeat prejudicial information it finds in its sources.
As a business, insulting customers or discriminating against them is something you definitely want to avoid.
Shortcomings in data protection
You also have to be careful when it comes to handling customer or employee data with generative AI.
For one, you have to ensure that your employees don’t input personal information into a public and unchecked GenAI model. There need to be very clear guidelines and use cases for what data they’re allowed to share with generative AI models.
But what about using generative AI for customer communication? If you’re using a model where you don’t control what happens with the customers’ personal data or private content of their messages information, that’s a no-go.
If you want to scale and automate business processes with generative AI, on-premise models or controlled solutions are a far safer option. These still give you access to the technology, but in a protected environment where you’re in charge of what happens with the data and can assign roles and responsibilities.
Safe business use cases for generative AI
At Sinch, we’ve developed several generative AI solutions that let you take full advantage of the technology without having to be concerned about safety.
Deploy a generative AI chatbot to answer FAQs
Do you enjoy setting up automated responses to answer frequently asked questions? Guess what? You really don’t have to!
Sinch’s Knowledge Base AI can take over. All you have to do is feed the bot a link to your FAQ page or upload a document, and only minutes later, the bot will be able to pull answers from there and pass them on to customers.
Since Knowledge Base AI uses generative AI, the answers won’t just be a copy-paste version of your documents, but a smooth reply. At the same time, the bot won’t go beyond the information you provide, so you never have to worry about made-up answers.
Bradlows, for example, southern Africa’s leading retailer for stylish furniture, implemented Knowledge Base AI as part of their web chatbot, Jaydee. Here, customers can either select a button related to a topic or simply type their question in the chat, to which Jaydee responds in a conversational way.
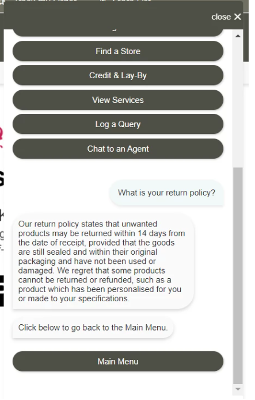
Generate personalized and localized marketing content
Struggling to find the right words for your email, SMS, or WhatsApp campaign? Let generative AI help you!
With our built-in generative AI tools for email, SMS, and WhatsApp, writing marketing copy has just become easier. You simply tell the AI generator what you want to write about, select a tone, language, and word limit – and the tool will generate engaging content for you.
All of this happens in a safe and secure environment, and you can always review everything before sending it out to customers.
The future of generative AI for businesses
Generative AI holds a lot of potential for businesses. It certainly won’t replace humans, but it can take over tedious manual tasks, scale processes, and enhance creativity.
“It’s not always about generating an end product, but more so about giving people tools to be more creative.”
– Fréderic Godin, Head of AI, Sinch
And with the fast development of the technology, these tools have become accessible to businesses of all sizes without requiring IT resources.
Nevertheless, it’s important to also be aware of the limitations and risks of GenAI and ensure that you’re using secure solutions that protect your customers, your employees, and your business.
Reach out to our specialists, and we’ll walk you through the best generative AI solutions for your business.
FAQs about generative AI
What is generative AI?
Generative AI (GenAI) is a type of AI technology that can create various types of content (images, text, videos, code, etc.) based on user prompts.
Is ChatGPT a generative AI?
Yes, ChatGPT is a form of generative AI that helps users with content generation and information gathering. It also uses conversational AI in its interaction with users.
What are some examples of generative AI?
Some popular generative AI models are ChatGPT, Midjourney, Gemini, and Jasper.
Why is generative AI important?
Generative AI tools can reduce the resources needed to create content and boost, both, creativity and productivity. Ultimately, the technology has the potential to change how content is created, how people work, and how businesses are run.
How can businesses use generative AI?
Businesses can use GenAI to automate processes, reduce workload, and enhance their team’s creativity. For example, businesses can use generative AI to automate customer support, enhance employee education, support content marketing, optimize developer code, and optimize data analytics.
Is it safe to use GenAI?
While the technology holds a lot of promise, there are also limitations. As many GenAI models don’t reveal their sources, they lack transparency. Without proper controls and regulations in place, it’s not guaranteed that user data is processed safely.
There are also instances where the AI “hallucinates” answers. That means that it gives an answer based on what it thinks is the most likely to satisfy the user, regardless of whether it’s correct or not. It can also transfer biases and prejudices from its sources.
That’s why it’s important to ensure that you use a generative AI solution that was designed with safety in mind and gives you control over its output.